Transfer addiction, also known as cross-addiction or addiction transfer, is a phenomenon where individuals who have successfully overcome one addiction replace it with another. This transition can involve substituting one harmful behavior or substance with another that provides a similar psychological or emotional reward.
While transfer addiction is not a formal diagnosis in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), it's a concept observed in various addiction recovery settings. Due to this, we feel that it warrants attention. Here at Recovery Cove, we find that transfer addiction is not unusual, especially in the first year of recovery when individuals are looking for ways to cope and still haven’t broken free of unhealthy habits.
Below is more information about transfer addiction and how to address it. Just as it’s possible to overcome substance use, it is possible to overcome transfer addiction.
Recognizing Transfer Addiction
Transfer addiction can manifest in various forms, and not all may appear harmful, at least at first. But remember, it’s not about the activity per se, but rather the individual’s relationship with it.
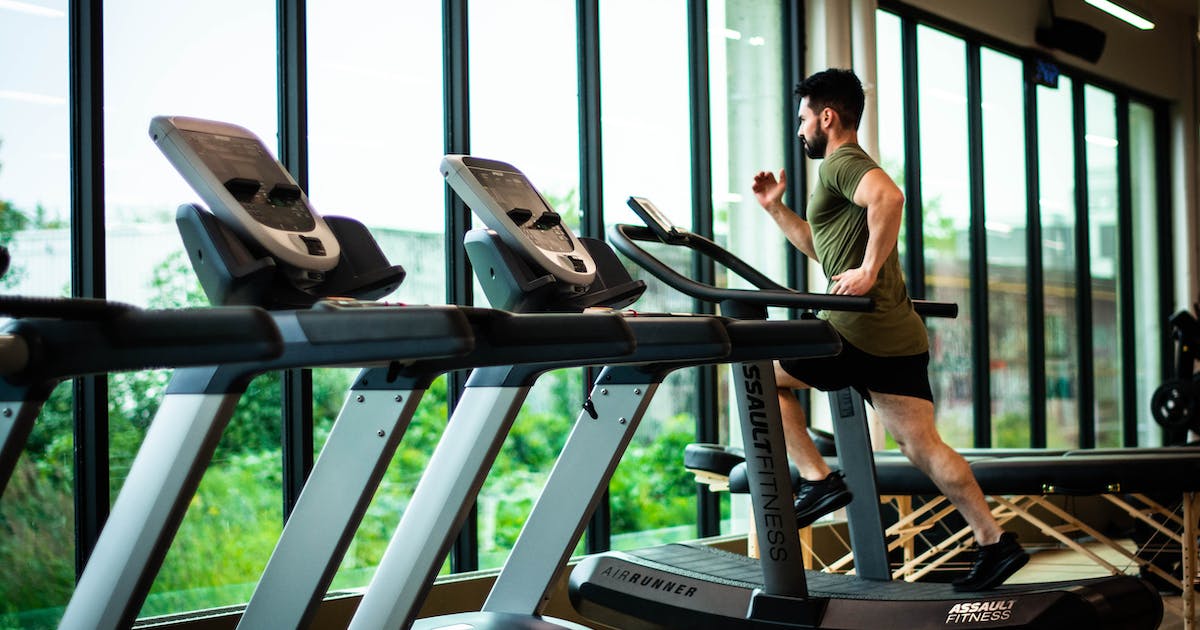
For example, you might notice that your loved one is taking a strong interest in exercise. Keeping active is physically and mentally healthy, as well as a great tool for staying sober. However, the problem comes when your loved one starts becoming obsessed with exercise.
The unhealthy behaviors they had with substance use (e.g., not being able to cut down, developing tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, neglecting other responsibilities) are now manifesting in exercise.
Here are some examples of transfer addictions:
- Substance substitution. Individuals recovering from substance use may replace their drug of choice with another substance, such as alcohol, nicotine, prescription medications or even non-substance-related behaviors like gambling or excessive eating.
- Behavioral substitution. Instead of turning to substances, some individuals may develop compulsive behaviors, such as overeating, shopping, excessive exercise or engaging in risky sexual activities, to cope with underlying emotional issues or cravings.
- Activity substitution. People may replace their addictive behaviors with seemingly positive activities, such as workaholism, excessive involvement in hobbies or interests or obsessive focus on self-improvement pursuits like extreme dieting or exercise regimes.
Causes of Transfer Addiction
Transfer addiction is complex and involves several factors:
Underlying psychological issues
Individuals grappling with unresolved emotional issues, trauma or mental health disorders may seek solace or distraction through addictive behaviors, leading to the transfer of addiction from one substance or behavior to another.
Neurobiological factors
Neurochemical imbalances in the brain's reward system, which are common in individuals with addiction, can predispose them to seeking alternative sources of pleasure or relief when abstaining from their primary addiction.
Environmental influences
Social factors, peer pressure, family dynamics and exposure to stressors or triggers in the individual's environment can play a role in the development of transfer addiction.
Lack of coping skills
Inadequate coping mechanisms to manage stress, negative emotions or cravings may lead individuals to resort to addictive behaviors as a means of self-soothing or escape.
Addressing Transfer Addiction
Recognizing and addressing transfer addiction requires a comprehensive approach that addresses underlying psychological, emotional and behavioral factors. As long as your loved one is receiving continuing care through an outpatient program, they’ll have access to resources and support that can address cross-addictions. If they aren’t receiving aftercare, you’ll want to consider getting them additional support.
Therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) and motivational interviewing can help individuals explore underlying triggers, develop healthier coping strategies and challenge distorted beliefs. It’s important that your loved one continues with their therapy regimen so that they are aware of their behaviors. Support groups can also be beneficial, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA).
Self-care is another crucial component, and this involves managing stress levels, staying physically active, getting adequate sleep and eating a nutritious diet. Mind-body practices like mindfulness meditation and yoga can help individuals create a holistic approach to well-being and reduce the likelihood of transferring addiction to other behaviors and substances.
Outpatient Services that Provide Continued Support
Transfer addiction is a complex phenomenon that underscores the intricate interplay of psychological, biological and environmental factors in addiction recovery. By raising awareness, fostering self-awareness and providing comprehensive support and resources, individuals can navigate the challenges of transfer addiction and embark on a path of sustainable recovery.
To learn more about the addiction treatment services available through Recovery Cove, contact us today at 484-549-COVE. We provide a full continuum of care that ensures our clients receive support through every phase of the recovery journey. We feel that with the right support, an emphasis on self-care and assistance building a sober lifestyle, our clients can remain truly free of addiction.